https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/smb/cloud-and-systems-management/network-automation-and-management/Installing_Postfix_Mail_Server_on_a_Raspberry_Pi.html
Objective
This document provides instructions on how to flash Asterisk onto an SD card and install Webmin and Postfix Mail Server. The goal is to install Postfix Mail Server onto a Raspberry Pi for testing purposes.
What is Webmin?
Webmin is a Graphical User Interface (GUI) for system administration for Unix-like system. Unix is an operating system that supports and allows for multitasking and multiuser functionality. You can easily install modules on Webmin such as Postfix Mail Server, Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) server, Procmail Mail filter, Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) VPN Server, and many more. You can also set up user accounts, DNS, file sharing, and other configurations that you need instead of having to manually edit each Unix configuration file. This is a good solution if you don’t like working with command lines and would rather use the GUI to help you configure and add new functionality.
To learn more about Webmin, click here.
What is Postfix Mail Server?
Postfix Mail Server is an open-source mail transfer agent. It is an application that is used to send and receive mail. Postfix Mail Server can be used with other modules such as Dovecot. Dovecot is an open-source Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) and Post Office Protocol 3 (POP3) server that is used as a mail storage server.
To learn more about postfix, click here.
Why do I want to Install Postfix Mail Server?
Everyone uses email. Users can host their own mail server, or they can go with a third-party provider. One of the biggest questions that people have when using a third-party provider is, “Am I comfortable with that?” Most users would probably want to use a third-party provider because their security is better than what they have at their home or at their small business; but some users would rather host it internally. When hosting your own mail server, you have complete control over your own data.
Additionally, hosting your own mail server means you get to control your own email address with your domain name (i.e. Bob@esupport.com). Which for business presentation looks better than reaching out with a third-party domain name (i.e. Bob@hotmail.com). There are a lot of choices that the users have when hosting their own mail server. There is Exchange, Sendmail, Groupwise, Postfix, and many more. Some servers are free, but some are not. In this case, Postfix is a free and open-source mail server that users can install on their Raspberry Pi.
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi (Pi 3 B+, Pi 3, Pi 2, B+, B, and A model – for more information, check out: raspberry-asterisk.org)
- Asterisk Image
- Etcher
- SD card (32 GB minimum)
- SD card adapter (optional – if your device has an SD card port)
- Domain Name (optional – depending on your use case)
Table of Contents
- Installing Asterisk on the Raspberry Pi
- Connecting to the Raspberry Pi using SSH
- Installing Webmin on the Raspberry Pi
- Accessing Webmin and Installing Postfix Mail Server
- Conclusion
Installing Asterisk on the Raspberry Pi
Step 1
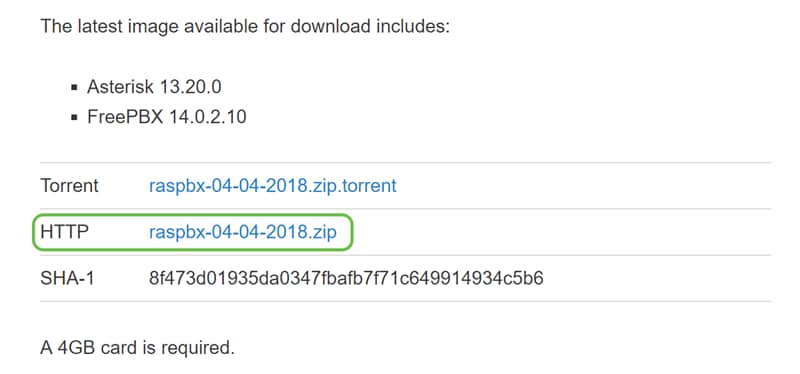
In the raspberry-asterisk downloads page, scroll down till you see the latest image available for download. In this example, we selected the raspbx-04-04-2018.zip next to the HTTP field. The zip file should start installing.
Step 2
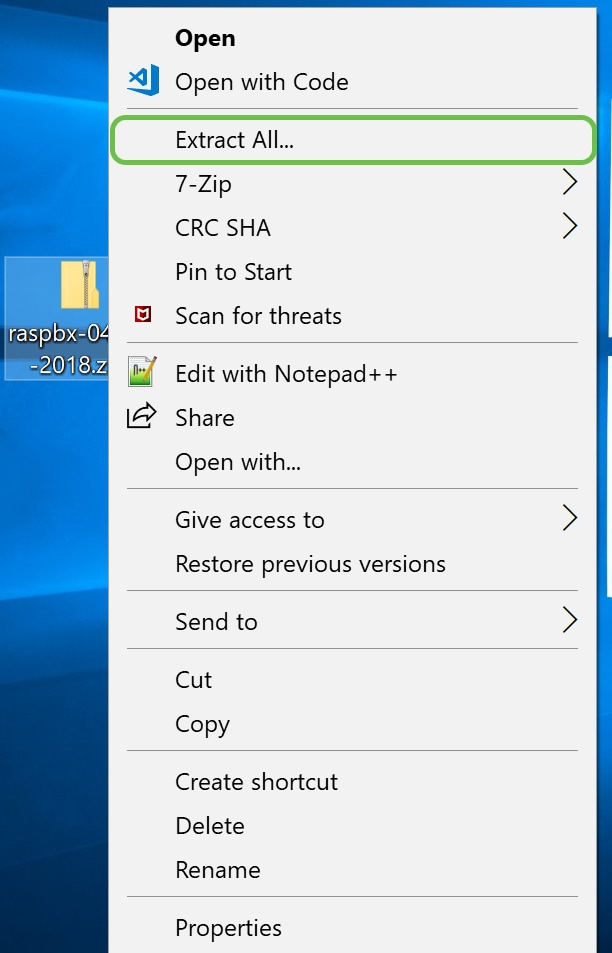
Once you have downloaded the zip file, navigate to the location of the zip file. Right-click the zip file and select Extract All….
Step 3
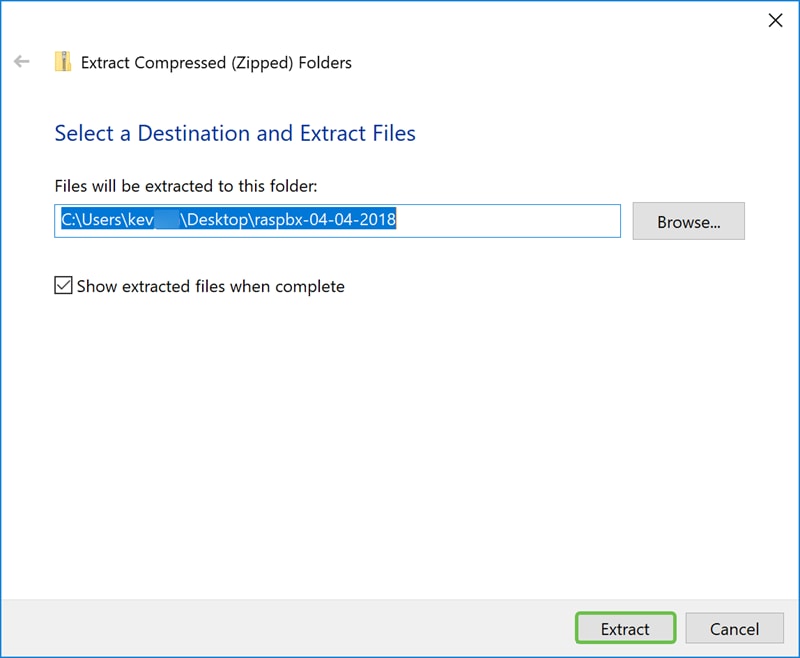
An Extract Compressed (Zipped) Folders window should appear. Click Extract to extract the zip file in the folder that it is currently in.
Step 4
Once the file has been extracted. You should see the unzipped folder.
Step 5
Run balenaEtcher.
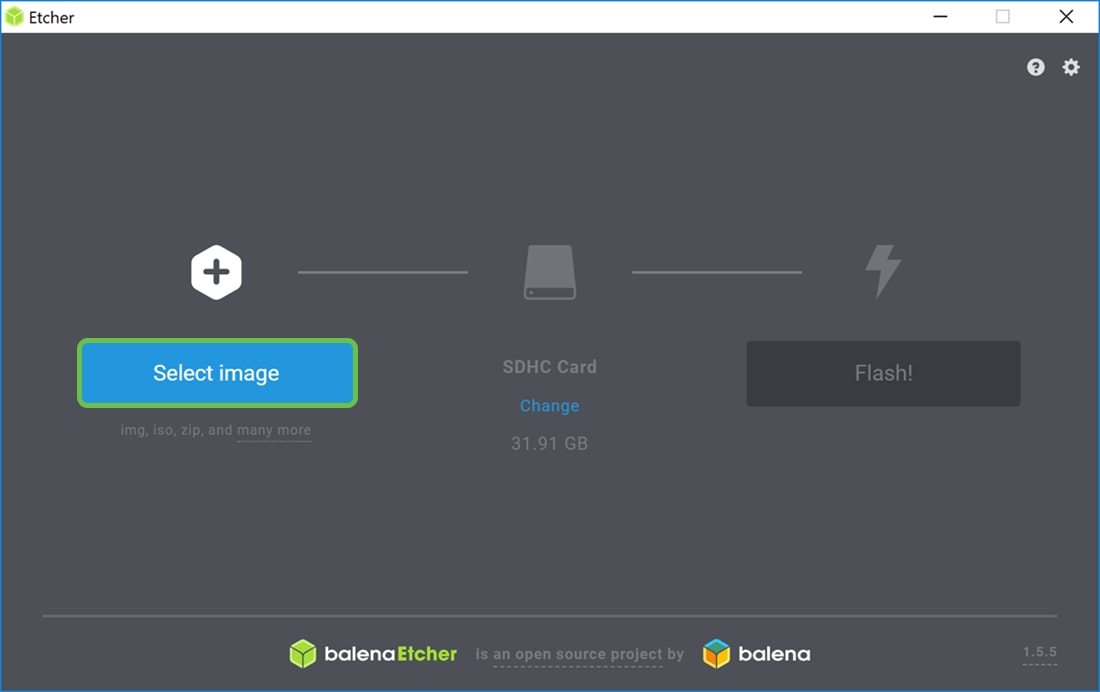
Step 6
The Etcher window should appear. Click Select image.
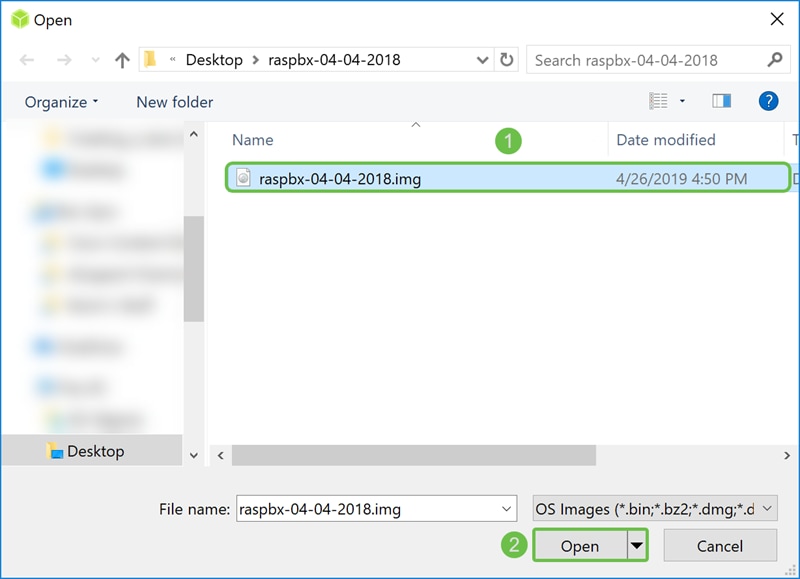
Step 7
The Open window appears. Navigate to the location of the raspbx image. Select the raspbx-04-04-2018.img and click Open.
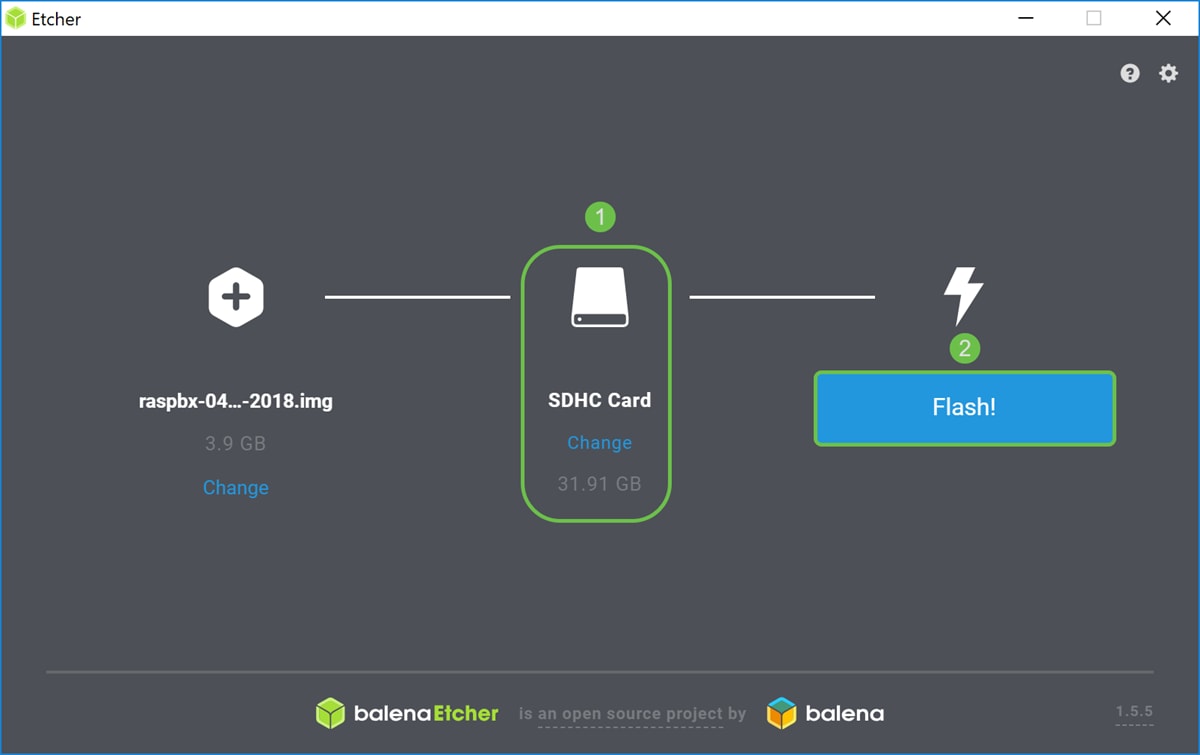
Step 8
Make sure your SD card is selected. Click Change to select a different SD card. Click Flash! when you are ready to flash the raspbx image to your SD card. It will take some time to flash the image onto your SD card. Please do not interrupt it. It should prompt you when it is finished flashing the image onto your SD card.
You should now have successfully imaged your SD card with the raspbx image.
Connecting to the Raspberry Pi using SSH
Step 1
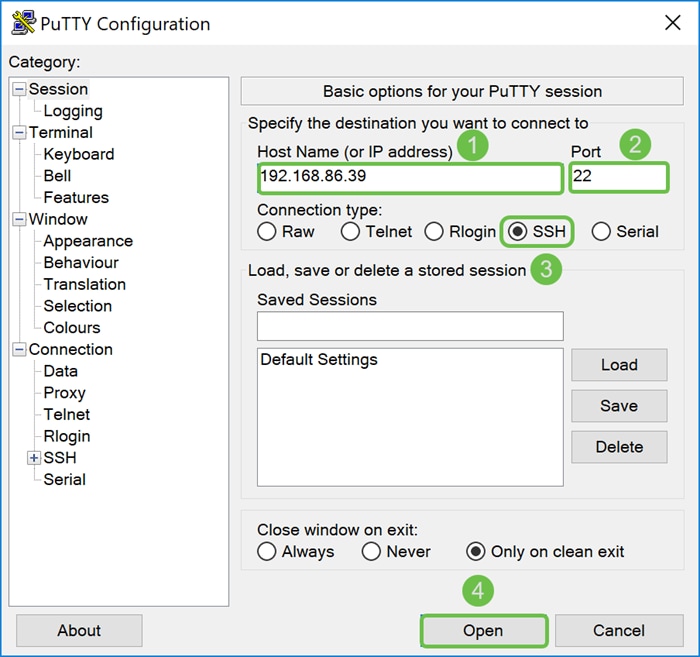
Connect to your Raspberry Pi by Secure Shell (SSH) or connect your Raspberry Pi to a computer monitor via HDMI. Before you can access your Raspberry Pi using SSH, you would need to know the IP address of the Raspberry Pi. In this example, PuTTY was used to SSH into the Raspberry Pi.
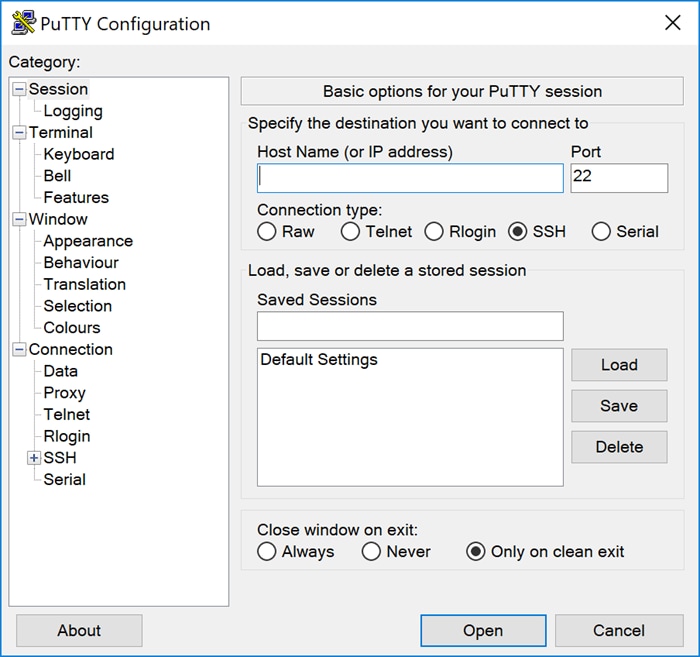
Step 2
Enter the IP address of your Raspberry Pi in the Host Name (or IP address) field. Ensure that the port is 22 and SSH is selected as the Connection Type. Click Open to start the session.
Step 3
A PuTTY Security Alert will appear. Click Yes to continue with the connection.
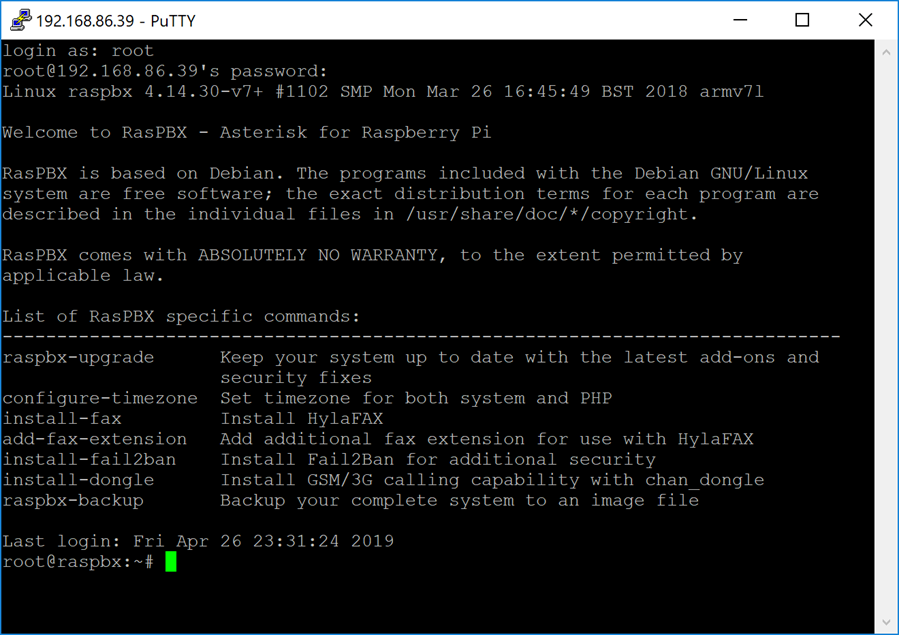
Step 4. You will be prompted with a login. Enter the username root and raspberry as the default password.
Installing Webmin on the Raspberry Pi
Some commands we will be using can be found on this page. For the most updated commands, refer to the link provided.
Step 1
Enter the following command to install dependencies. When prompted to continue, press y on your keyboard to continue.
sudo apt-get install perl libnet-ssleay-perl openssl libauthen-pam-perl libpam-runtime libio-pty-perl apt-show-versions python 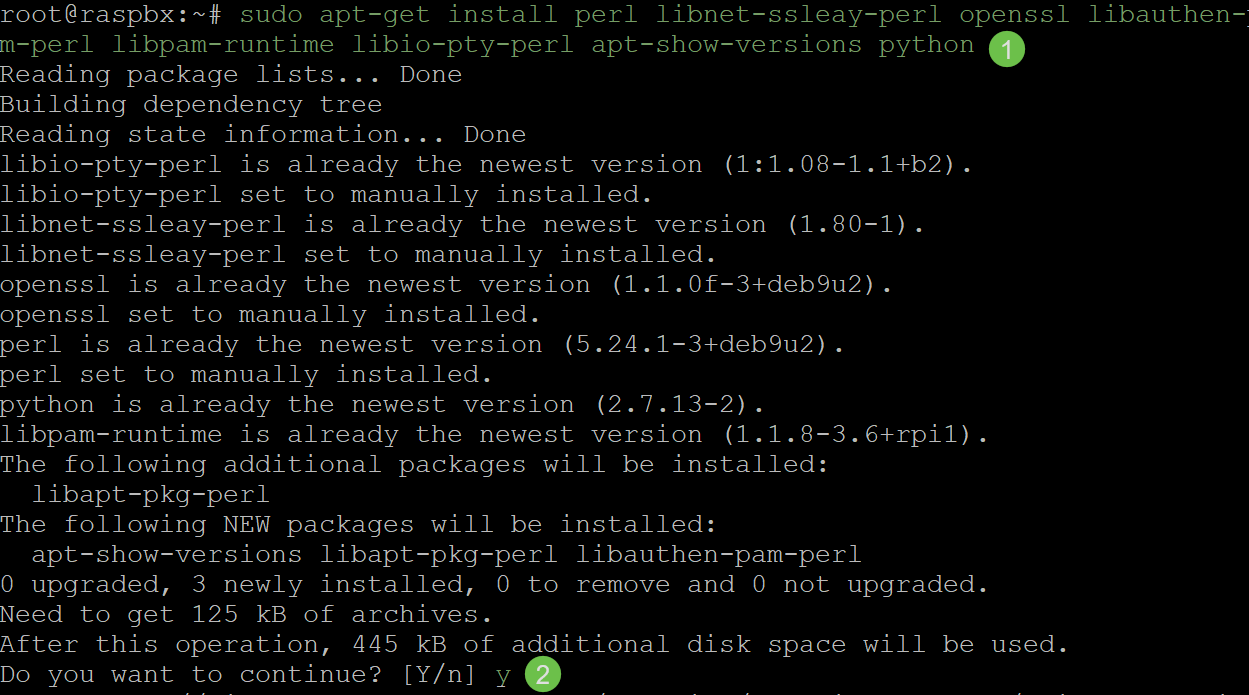
Step 2
Enter the command below to download the DEB version of Webmin into the Raspberry Pi. A DEB file extension is a Debian Software Package file. This is mainly used in Unix-based operating system which contains archives for executable files, documentation, and libraries.
wget http://prdownloads.sourceforge.net/webadmin/webmin_1.900_all.deb 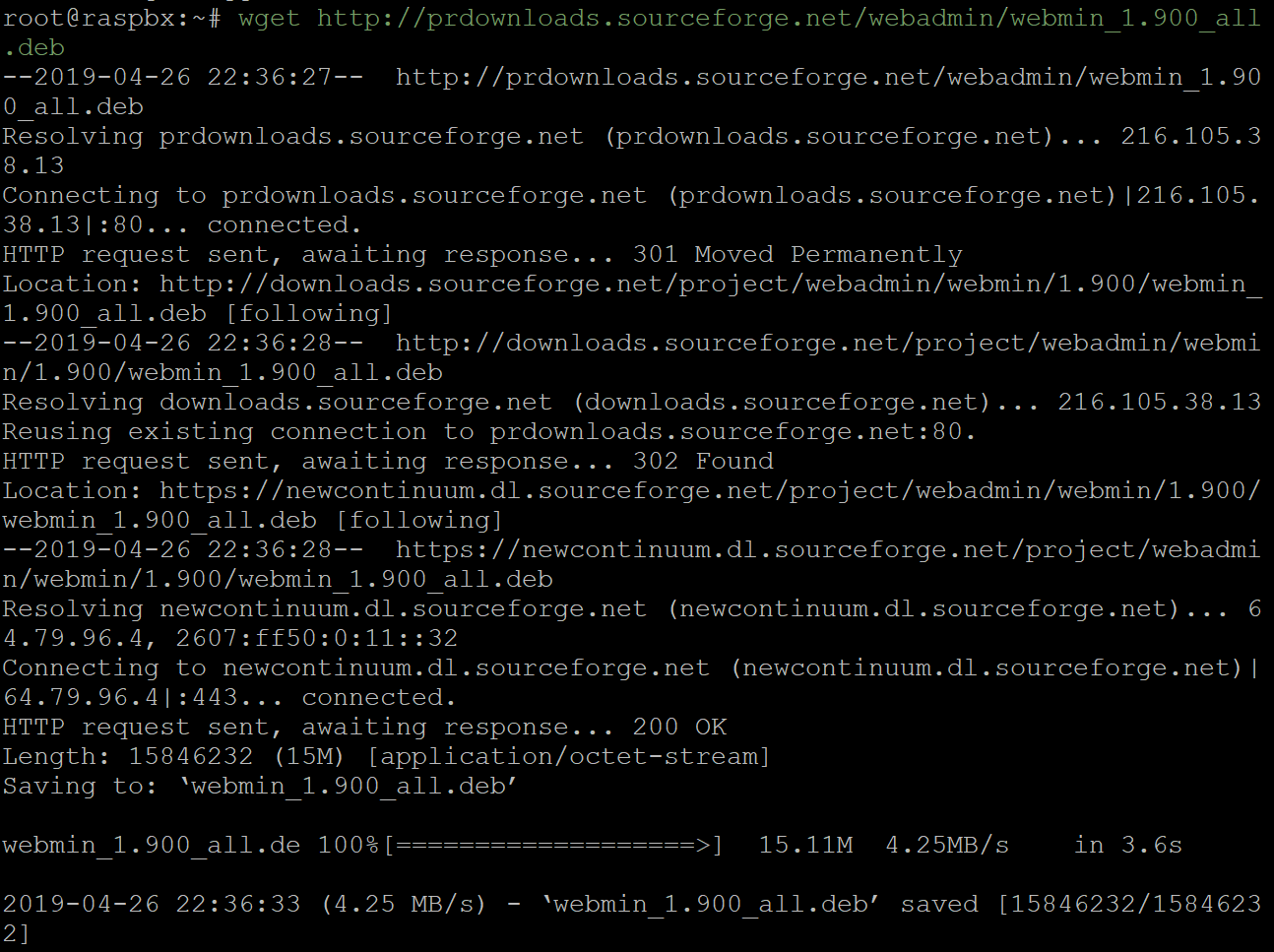
Step 3
Enter the command below to install Webmin.

You should have successfully installed Webmin on your Raspberry Pi.
Accessing Webmin and Installing Postfix Mail Server
Step 1
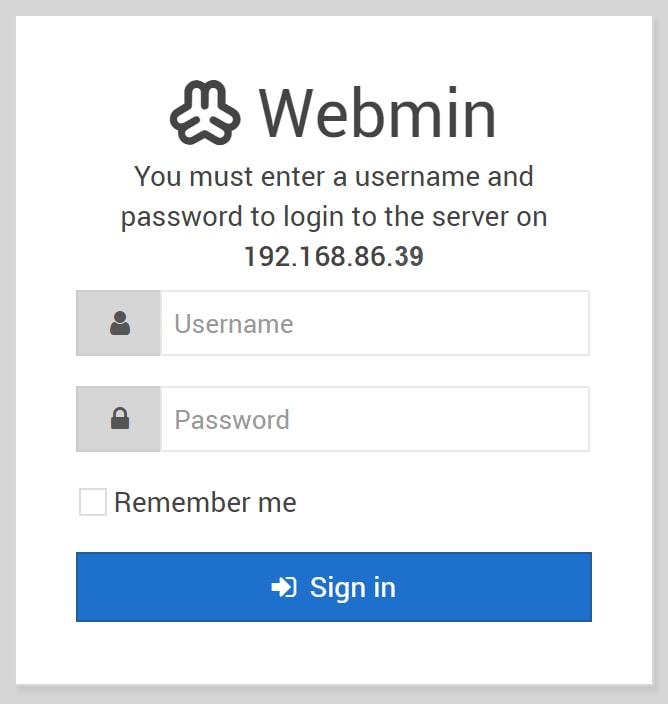
Enter https://IP_address_of_your_raspberry_pi:10000 in the URL of your web browser to access the web page of Webmin. In this example, https://192.168.86.39:10000 was entered.
Step 2
Log in to the web configuration page of Webmin.
Note: The username is set to root and the password is your current password for root. If you have changed your password in step 4 of Connecting to the Raspberry Pi using SSH section, then enter the password that you have changed.
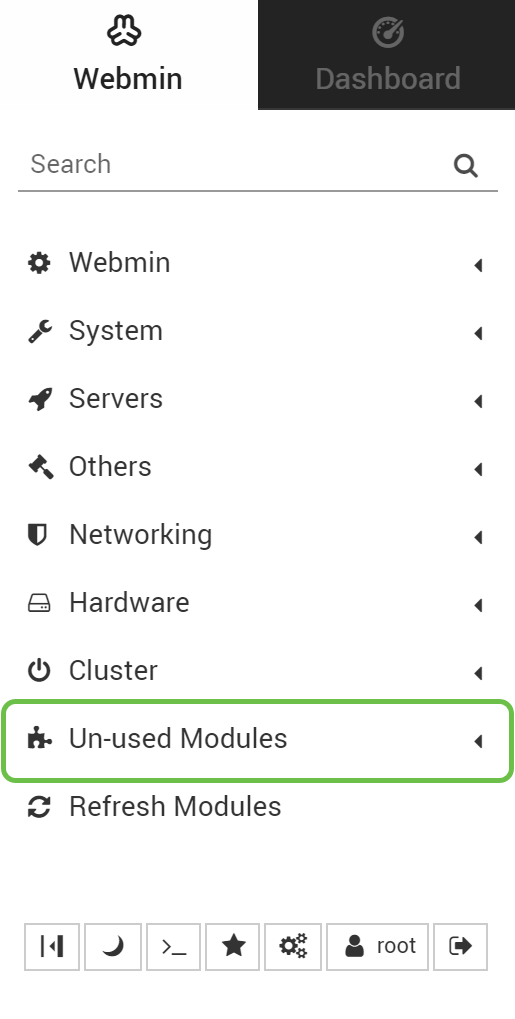
Step 3
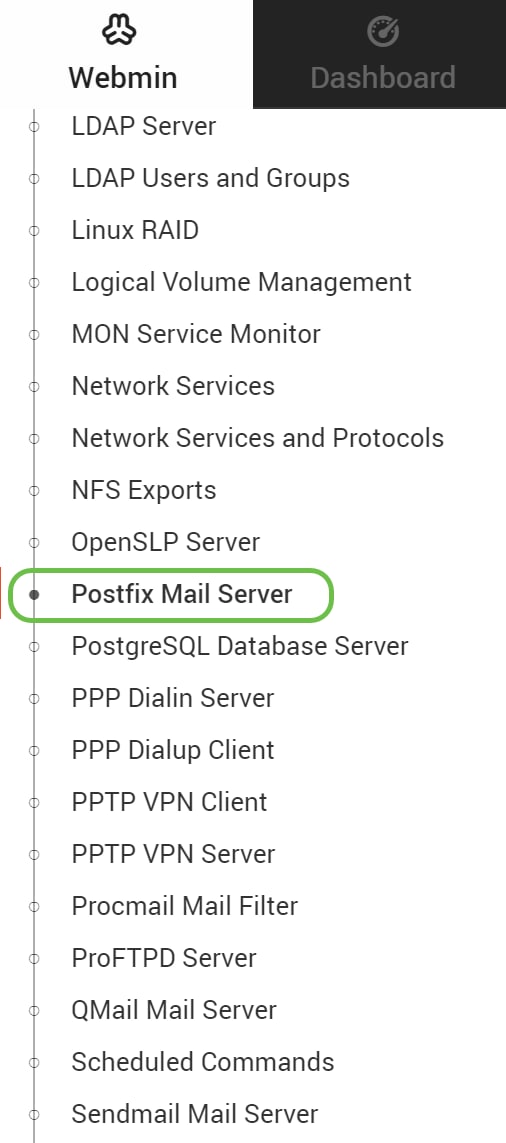
In the Webmin tab, click Un-used Modules drop-down list.
Step 4
In the Un-used Modules drop-down list, find Postfix Mail Server and click on it.
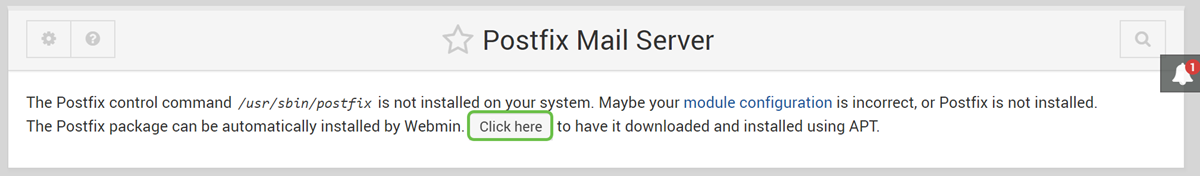
Step 5
In the Postfix Mail Server, click the Click here button to download and install Postfix. It will look for packages that you haven’t installed yet.
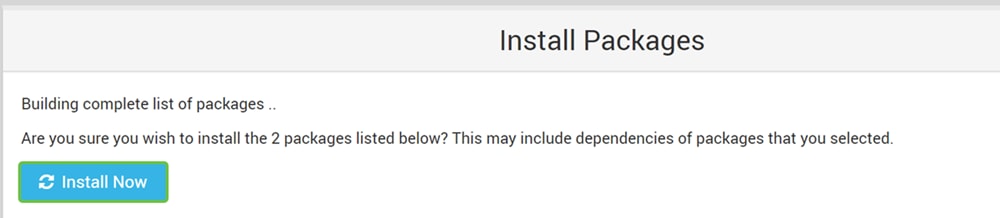
Step 6
Click the Install Now button.
Step 7
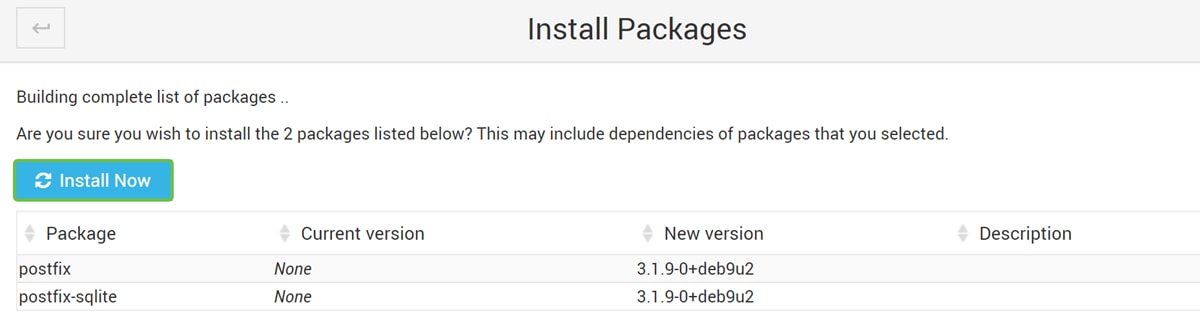
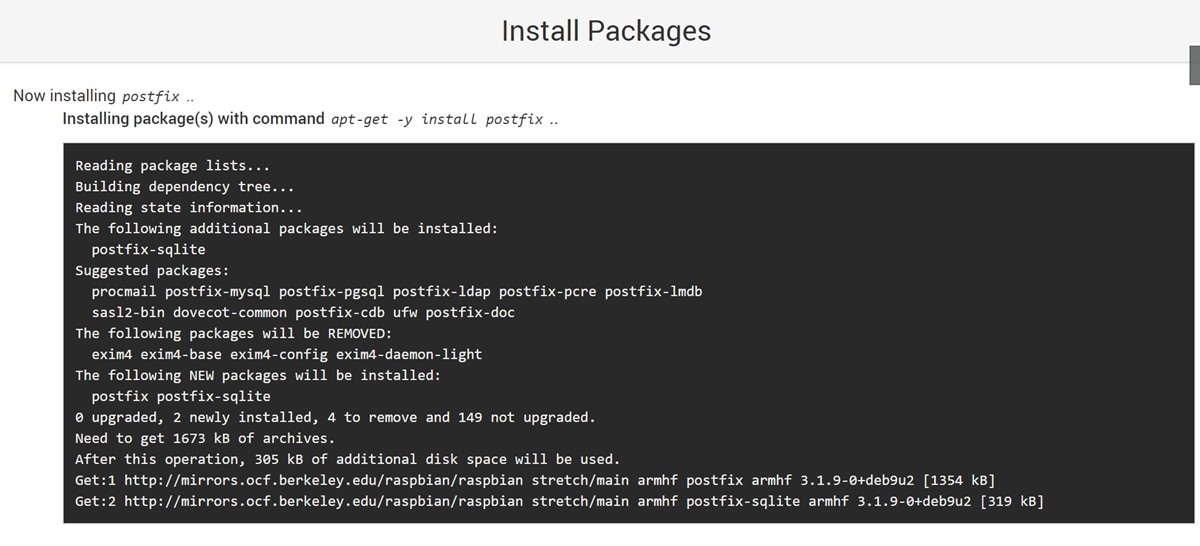
A list of packages will appear showing the packages that you will be installing. If the install has not started, click Install Now button again to start the installation.
Step 8
Postfix should be installing. You should see something like the image below.
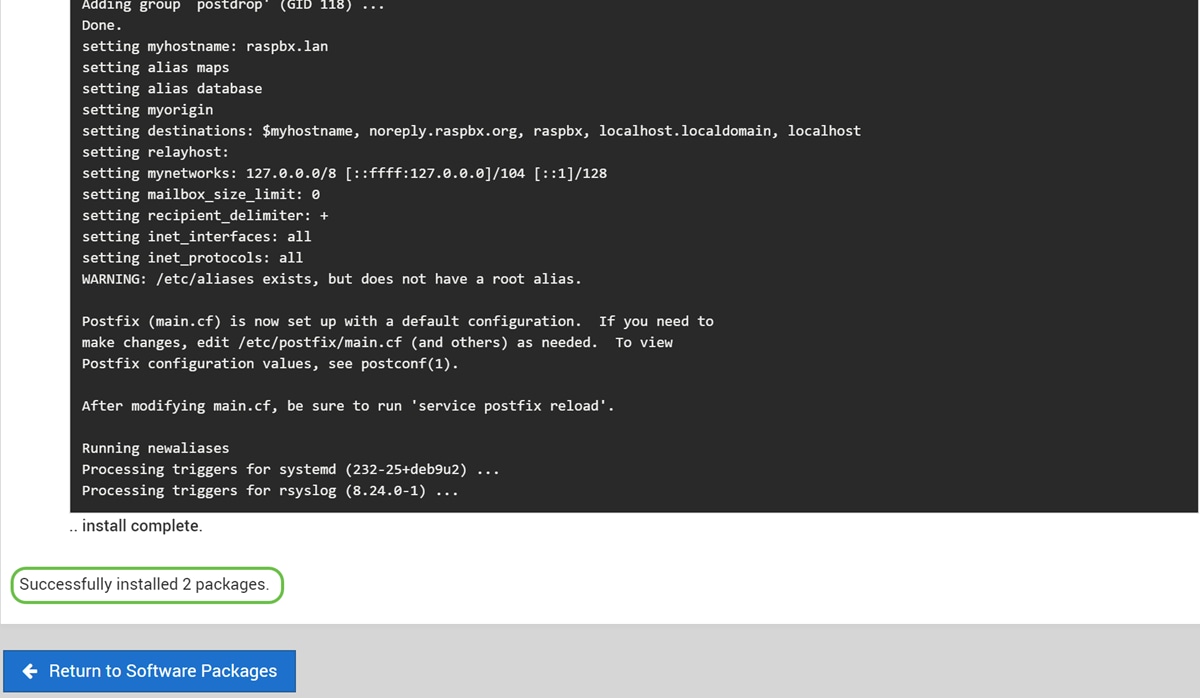
Step 9
Once Postfix has been installed, you should get a notification at the bottom stating that “install complete” or “Successfully installed 2 packages.”
Step 10
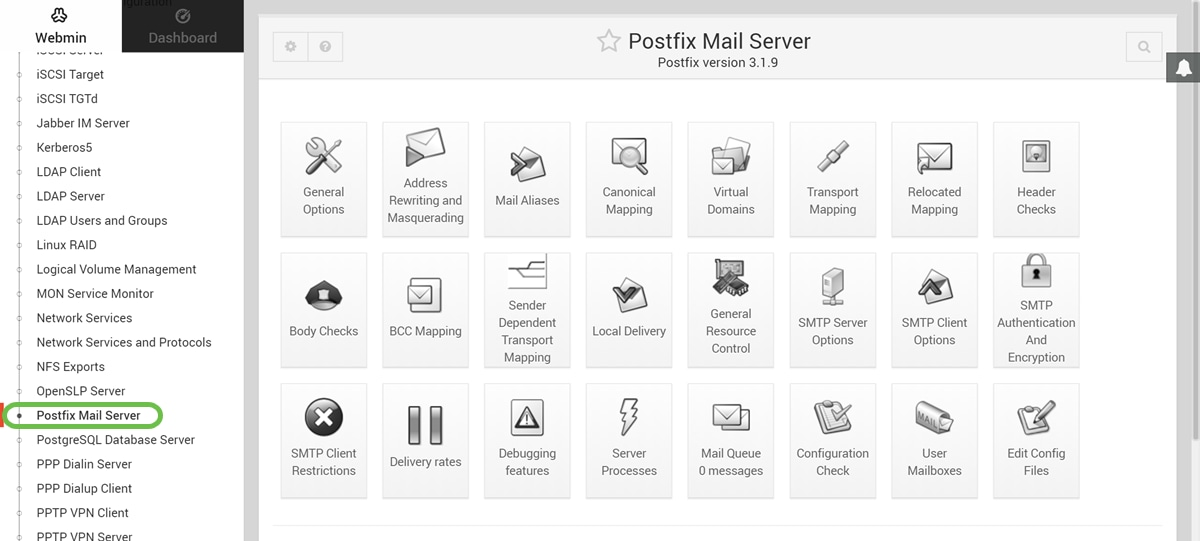
Navigate to Postfix Mail Server on the left side menu. Postfix Mail Server may be in the Servers or Un-used Modules drop-down list. In this example, Postfix Mail Server was in Un-used Modules drop-down list.
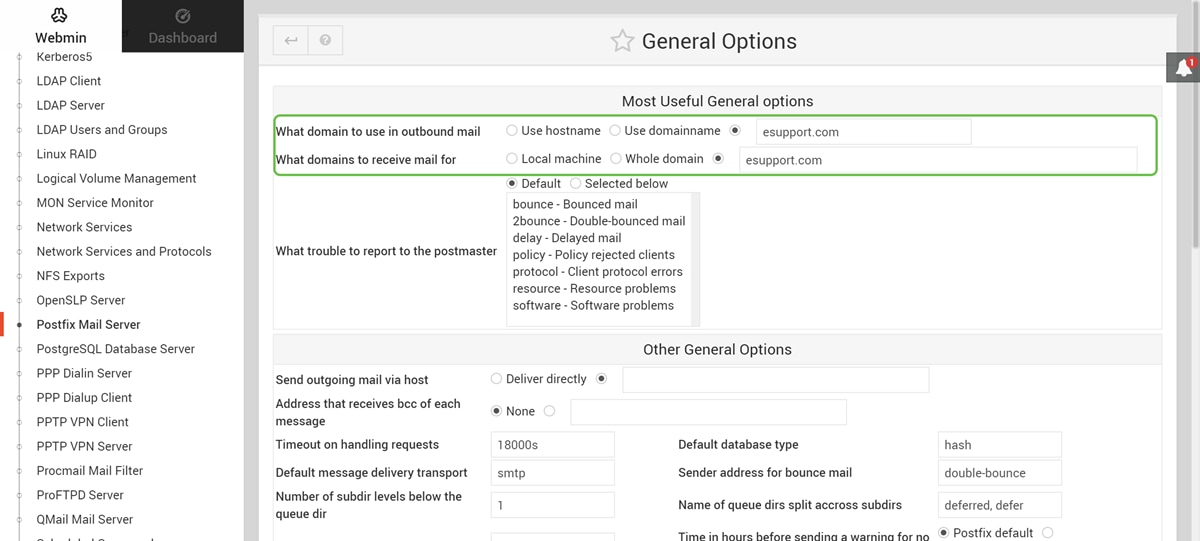
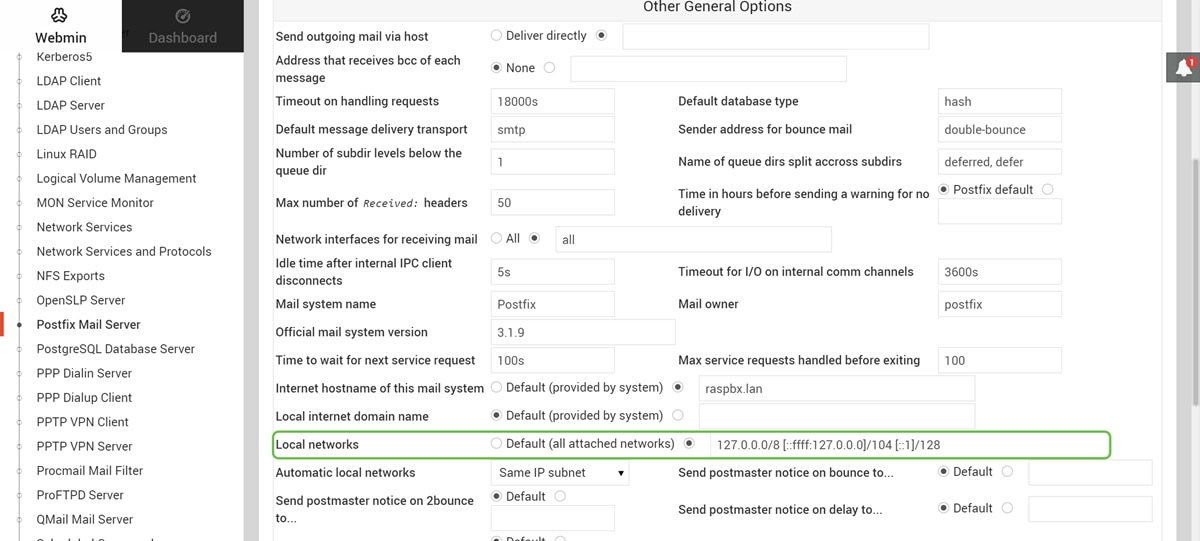
You should have successfully installed Postfix Mail Server on the Raspberry Pi. To start providing mail service with Postfix, there are three configurations that need to be configured in most cases. Click General Options, then configure What domain to use in outbound mail, What domains to receive mail for, and local networks. Click the Save and Apply button to save your change.
To learn more about it, please see Webmin’s documentation on Postfix Basic Configuration.
Conclusion
You should have successfully installed Postfix Mail Server on your Raspberry Pi.
Additional Information
If you’re interested in different approaches but still using Raspberry Pi, check out these tutorials:
Simplified tutorial – Make a Mail Server Out of Your Raspberry Pi 3
In-depth tutorial with other features: Sam Hobbs - Raspberry Pi Email Server Part 1: Postfix tutorial
To learn about creating a basic voice network using a Raspberry Pi, click here.
댓글 0
| 번호 | 제목 | 글쓴이 | 날짜 | 조회 수 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | [Linux] 일반 계정에서 SUDO 사용 및 SUDOERS 설정 하기 | proin | 2020.09.09 | 0 |
| 9 | 리눅스 sudo 사용자 추가하기 | proin | 2020.09.09 | 0 |
| 8 | Can I install PHP 5.3.5 on Ubuntu Server 18.04 LTS? | proin | 2020.09.06 | 0 |
| 7 | 리눅스(Linux) - 사용자와 권한 | proin | 2020.08.19 | 1 |
| 6 | [윈도우 리눅스 파일 공유] 삼바란 무엇인가. 리눅스에 삼바(SAMBA) 설치하는 법, 리눅스 삼바서버 설치 및 사용방법 | proin | 2020.08.19 | 0 |
| 5 | 파일 시스템 복구 (dump & Restore) | proin | 2020.08.18 | 0 |
| 4 | 리눅스 기본명령어 - restore | proin | 2020.08.18 | 0 |
| 3 | 리눅스 백업 명령어 | proin | 2020.08.18 | 0 |
| » | Installing Postfix Mail Server on a Raspberry Pi | proin | 2020.07.07 | 0 |
| 1 | JMeter로 웹 스트레스 테스트 | proin | 2020.03.10 | 0 |